If you’re feeling unsure about corporate tax deductible vs non deductible expenses in the UAE, you’re not alone. Pinpointing which costs your business can legally claim as deductions will help lower your taxable base and, in turn, reduce what you owe. On the flip side, mixing in non-deductible expenses could lead to compliance issues or unexpected payments later. In this guide, you’ll discover which expenses typically qualify, which ones don’t, and how to maintain solid records so your business stays on the right side of the tax laws.
Understand UAE Corporate Tax
Like many countries, the UAE has introduced a corporate tax regime to generate public revenue while still offering attractive incentives for global investors. The tax framework aims to be straightforward, but it’s essential to grasp the basics before you dive into the details of allowable and disallowed expenses. Corporate taxation in the UAE can vary based on factors like business activity, legal structure, and location (mainland or free zone).
- Corporate Tax Basics
- Applies to: Most UAE-registered companies, subject to specific thresholds and exemptions
- Rate: The corporate tax rate depends on current regulations, so verifying up-to-date details with official sources is wise
- Scope: Profits on worldwide income may be taxable if your company is based in the UAE, though free zones often enjoy favorable tax benefits
- Relevance of Deductible Expenses
- Directly lowers your taxable income
- Frees up funds for growth or reinvestment
- Encourages transparency and good financial practices

If you’re just embarking on your entrepreneurial journey in the UAE, it helps to understand the foundational aspects of your business structure. Some setups come with different reporting obligations. You can learn more about your company formation options by checking out how to setup a business in the uae and types of business licenses in the uae.
Identify Tax-Deductible Expenses
Tax-deductible expenses are those the UAE’s corporate tax regulations typically allow you to subtract from your revenue when calculating net taxable profits. In general, the expense must be legitimate, necessary for your business, and backed by proper documentation. Let’s walk through common categories that often qualify.
Operational and Administrative Costs
Day-to-day running costs usually fall under the deductible umbrella if they are integral to your core business. These can include:
- Office rent or lease payments
- Utility bills like electricity, water, and internet
- General office supplies (paper, ink cartridges, small equipment)
- Costs associated with staff recruitment and training
However, you’ll want to maintain clear receipts, invoices, and payment confirmations. If you’re not confident in your record-keeping system, consider professional accounting and bookkeeping solutions. Reliable bookkeeping helps you stay organized throughout the year rather than scrambling at tax time.
Identify Tax-Deductible Expenses
Tax-deductible expenses are those the UAE’s corporate tax regulations typically allow you to subtract from your revenue when calculating net taxable profits. In general, the expense must be legitimate, necessary for your business, and backed by proper documentation. Let’s walk through common categories that often qualify.
Operational and Administrative Costs
Day-to-day running costs usually fall under the deductible umbrella if they are integral to your core business. These can include:
- Office rent or lease payments
- Utility bills like electricity, water, and internet
- General office supplies (paper, ink cartridges, small equipment)
- Costs associated with staff recruitment and training

However, you’ll want to maintain clear receipts, invoices, and payment confirmations. If you’re not confident in your record-keeping system, consider professional accounting and bookkeeping solutions. Reliable bookkeeping helps you stay organized
Employee Salaries and Benefits
Paying your employees is one of the largest business expenses you’ll have. In most cases, these costs are deductible, including wages, bonuses, and certain benefits like health insurance. The UAE typically permits businesses to deduct these payroll-related expenses as long as the payments align with written employment contracts or official offers.
- Salary, bonuses, and gratuities
- Healthcare contributions
- Approved allowances or stipends
One caveat: excessive or unsubstantiated payments, especially to company owners or related parties, might be subject to scrutiny. Make sure all compensation is set at fair market rates and is well-documented.
Professional and Advisory Fees
Legal, advisory, and professional service fees are often overlooked when calculating deductions. But if you’re paying for guidance on workplace compliance, intellectual property rights, or similar tasks that serve the company’s operations, these should be deductible. Whether you’re working with lawyers, consultants, or auditors, keep itemized invoices for each service.
If you’re uncertain about the boundaries of specific advisory costs, you can seek expert tax consultancy. Professionals in this field clarify whether certain fees pivot between deductible and non-deductible based on your business activities.
Marketing and Advertising
Promoting your brand in a crowded market can be costly, but it’s usually a legitimate expenditure for businesses aiming to expand their customer base. Digital campaigns, social media ads, print materials, event sponsorships, and promotional merchandise typically qualify. Just be sure that any marketing outlay is genuinely intended to support or grow your enterprise.
Business Insurance
Insurance premiums for coverage like general liability, property, or professional indemnity can also factor into your deductions. These policies protect your company from potential losses, so the tax authorities generally view them as necessary expenses.
Recognize Non-Deductible Expenses
While the list of deductible costs can look generous, some items are definitely off-limits when it comes to corporate tax claims. Non-deductible expenses do not reduce your taxable income, and trying to include them could trigger penalties or fines. Here’s what to watch out for.
Personal and Private Costs
Your business funds should not cover personal items or other private spending. If you use corporate accounts to buy groceries, pay personal utility bills, or fund a family vacation, these expenses won’t be deductible. The key is to separate personal from business finances carefully. Many entrepreneurs rely on separate bank accounts, which makes tracking legitimate business outlays much simpler.
Fines and Penalties
Did you get a parking ticket or pay a fee for late license renewal? Unfortunately, government fines or penalties typically can’t be written off. The rationale is that the state wants to discourage bad behavior or negligence, so allowing tax deductions here would run counter to public policy.
Certain Entertainment and Hospitality
While some forms of hospitality might be allowed when directly related to business operations, it’s common for purely entertaining expenses to land on the non-deductible list. Fancy dinners or club memberships that don’t have a clear business nexus are often flagged. Always verify local guidelines because details can shift depending on regulatory changes.
Dividend Payments or Capital Withdrawals
Distributions to shareholders, partners, or yourself (as the business owner) don’t reduce the company’s taxable profit. These are not operating costs; they’re returns on investment or equity outflows. Keep a clear distinction between salaries (deductible) and dividends (non-deductible) to avoid confusion in your annual tax filings.
Donations Not Recognized by Authorities
Charitable giving often improves a company’s public image, but not all donations will be recognized for tax purposes. Some tax systems require your contributions to go to government-approved charities or foundations. If you want to make donations, confirm which organizations are on the approved list before claiming any tax deductions.
Use a Quick Reference Table
Staying on top of allowable vs disallowed expenses is simpler with a reference list. Here’s a brief snapshot:
| Expense Category | Deductible? | Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
Office Rent
|
Yes | Must be tied directly to business activities |
|
Utility Bills
|
Yes | Must be for business use only |
|
Employee Salaries/Benefits
|
Yes | Must reflect market rates, properly documented |
|
Marketing Costs
|
Yes, if business-related | Ensure link to actual promotions or brand awareness |
|
Professional Fees
|
Yes | Legal, consulting, tax consultancy, etc. |
|
Personal Expenses
|
No | Should be covered from personal funds |
|
Fines/Penalties
|
No | Encourages compliance, can’t be offset |
|
Dividends to Owners
|
No | Not considered a business expense |
|
Some Hospitality
|
No (or limited) | Depends on local rules, ensure direct business relevance |
Always double-check local regulations because tax laws evolve. If you’re looking to avoid slip-ups, specialized compliance services or an experienced consultant can offer updates as legislation changes.
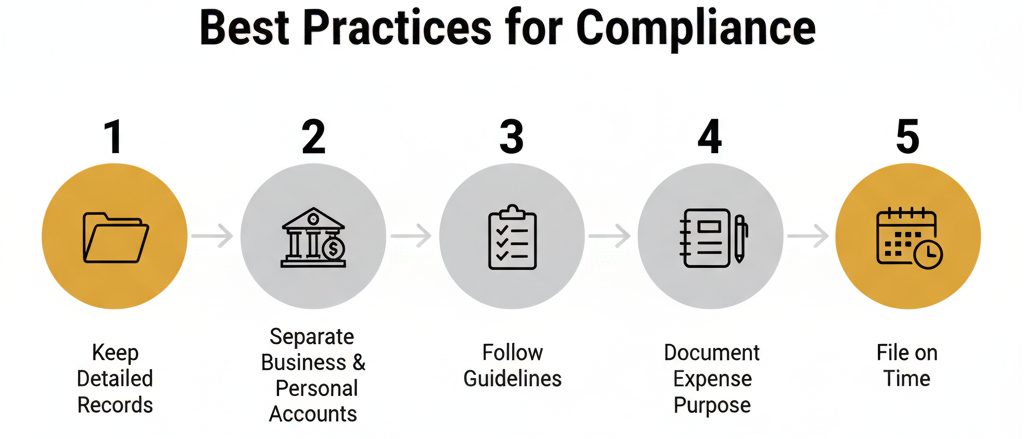
Incorporate Best Practices for Compliance
Now that you know which items typically qualify as corporate tax deductions, you’ll want to implement best practices to keep everything shipshape. Good systems and routines can protect you from the anxiety of last-minute scrambles or audits.
Keep Detailed Records
Track every invoice, receipt, and payment confirmation. Digital tools, cloud-based accounting software, or outsourced accounting and bookkeeping services can streamline your record-keeping. Sort expenses by category, attach digital copies, and label them with clear notes.
Separate Business and Personal Accounts
Mingling personal and corporate funds creates confusion and can invalidate deductions. Open dedicated corporate bank accounts and credit cards so you can confidently identify business-related transactions. Look into corporate banking solutions in the UAE that offer integrated features like expense tracking or consolidated statements.
Follow Official Guidelines
Government announcements, new directives, and official rule changes can alter what’s considered deductible or how you must file. Make it a habit to check official channels or work with advisors who stay on top of relevant notices. Frequent communication with tax consultancy experts can help you avoid falling behind.
Document Expense Purpose
You might know in your head why you paid for a certain item, but an auditor or tax official needs clarity in black and white. A simple note or memo on each receipt explaining its business purpose can make a big difference later.
File on Time
Missing deadlines or submitting incomplete forms can incur penalties, which are obviously not deductible. Set reminders for filing dates or create a calendar that outlines quarterly or annual submission timelines. Punctuality here is a major plus.
Develop a Long-Term Strategy
Your tax approach should align with your broader business goals. By prioritizing compliance and carefully planning your finances, you can reinvest savings in growth opportunities or strengthen your market position. It’s worth viewing good tax planning as an integral part of your overall success strategy.
- Forecast Your Expenses
- Estimate your costs for the coming quarters
- Identify which expenses are crucial to expansion
- Budget for non-deductible outlays so they don’t surprise you later
- Consult Professional Services
- Rely on specialists to draft or review your tax strategy
- Evaluate your corporate structure: will a mainland or free zone setup best match your needs?
- Assess the possibility of relocating or restructuring if the tax environment changes
- Consider Business Growth Options
- Reinforce your enterprise by reinvesting tax savings into research, product development, or staff training
- Explore new markets or tie-ups with partners who share compatible visions
- Stay agile so you can pivot quickly if tax laws shift or your company’s needs evolve
Every company has unique circumstances. Some might thrive with smaller, specialized teams, while others need a larger workforce to scale. If you’re unsure about how best to organize your resources for long-term stability, you can check out set up your business for long-term growth.
Avoid Common Pitfalls
Even if you think you understand the basic difference between allowable and disallowed expenses, there are still some traps that can trip you up. Here’s how to steer clear:
- Mixing Up Mixed-Use Items
- If you have expenses that serve both personal and business purposes, like a multipurpose phone plan, split the costs accurately. Only the business portion is deductible.
- Forgetting Exchange Rate Issues
- International transactions might involve currency conversions. Keep accurate records of the exchange rate on the date of payment, in case the tax authority requests documentation.
- Losing Supporting Documents
- It’s easy to misplace receipts or invoices. Snapshot them right away or use scanning apps.
- Delaying Corrections
- If you spot an error in your filings, correct it promptly. Waiting until the authorities find it could result in penalties.
Staying proactive is a lifesaver. If you notice a potential misstep or a gap in your processes, address it immediately. Timely action can help you avoid bigger problems down the road.
Explore Additional Resources
Staying compliant is easier when you have the right support. Here are a few next steps if you want more comprehensive assistance:
- Compliance Services: Ideal if you need end-to-end help with understanding regulations.
- Tax Consultancy: Perfect for deep dives into complex tax scenarios.
- Accounting And Bookkeeping: A must if you’d like to keep meticulous track of your deductible expenses year-round.
If you haven’t yet finalized your business structure, you could brainstorm whether a free zone company or a mainland setup fits your plans. Each has unique implications for taxation. You can learn more about that in mainland vs free zone.
Final Thoughts and Encouragement
Navigating the maze of corporate tax can feel daunting at first, but remember that these rules are designed to foster transparency and fairness. Once you master which expenses are deductible and which are off-limits, you’ll have a clearer path to effective budgeting and smooth compliance.
If you’re methodical about record-keeping, open with your advisors, and diligent about staying updated, tax season won’t be a panic-filled scramble. Instead, it can be another step in your company’s steady routine. After all, an informed approach to UAE corporate tax allows you to reinvest savings back into your venture, fueling the growth and innovation that keep you ahead in a competitive market.
Feel free to explore more resources or professional guidance if you need personalized help. Paying close attention to eligible and ineligible expenses might just be the simplest way to give your business a competitive edge. And when you need clarity on corporate tax deductible vs non deductible expenses, remember that being proactive and well-informed sets you up for success in the UAE’s thriving business landscape.
Poll – Get Expert Help
Would you prefer setting up alone or with expert help?
Great. Here is a simple guide to help you move forward.
Open the step-by-step guideWe can match you with a consultant for tailored support.
Schedule a consultation






