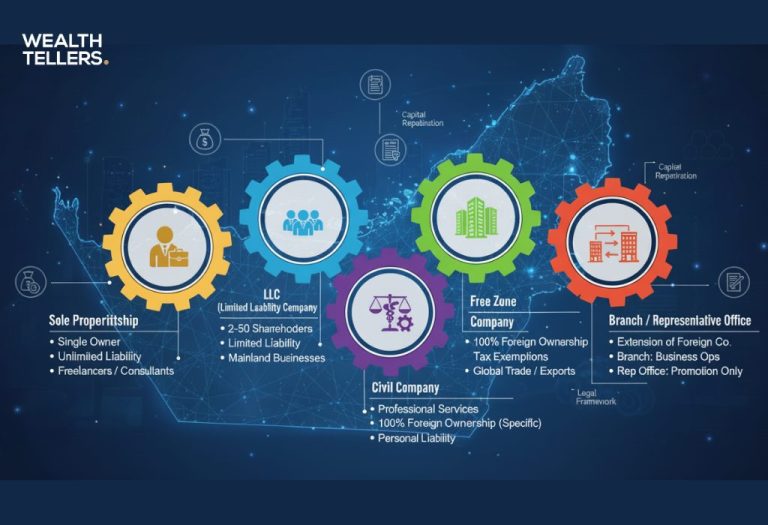
When you first explore business structures in the UAE, you’ll discover a wide range of options designed to accommodate different budgets, ownership preferences, and strategic goals. Whether you plan to launch a local shop, an international trading firm, or a specialized consultancy, choosing the right legal framework can make all the difference in shaping your level of control, the scope of your operations, and the overall cost of doing business. You’ll also find that the UAE’s pro-business environment offers favorable regulations and incentives, helping you operate more efficiently and remain competitive in the region.
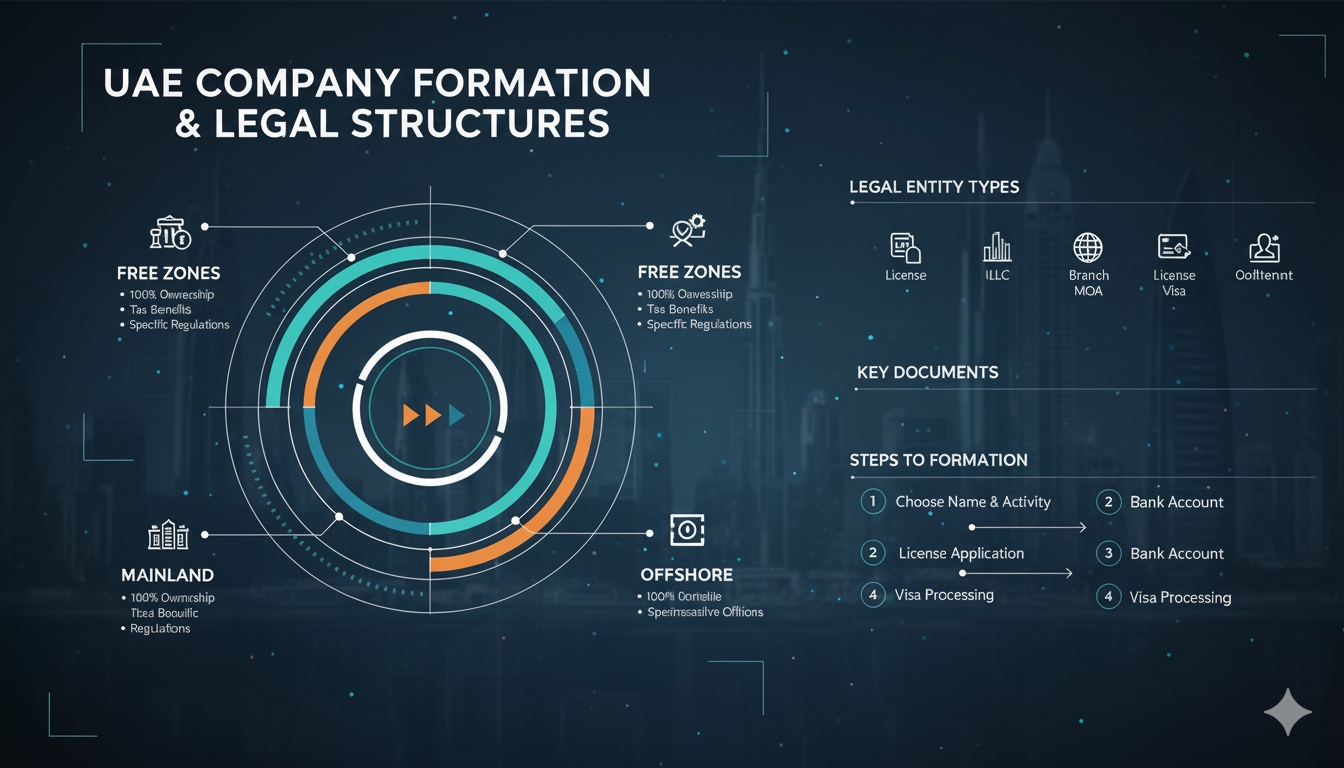
At first glance, it can feel overwhelming to navigate the ins and outs of UAE company formation. You might wonder about sponsor requirements, foreign ownership rules, or the process of acquiring trade licenses. In many cases, the type of business you intend to run will guide your decision, although your expansion goals and target markets also play important roles. Throughout this article, you’ll learn about five of the most common business structures in the UAE, along with each structure’s pros, cons, and key formation guidelines. By the end, you’ll have a clearer idea of which route best fits your vision. If you need deeper insight into how licensing works, you can also check out types of business licenses in the uae.
Quick way to choose a UAE business structure
Use this simple decision flow to narrow your best-fit option before you start paperwork.
Do you need to sell inside the UAE market?
If yes, a mainland setup or a branch office is usually the most direct route.
Is 100% foreign ownership your top priority?
Free zones are built for this, with streamlined processes and industry-focused support.
Are you mostly doing international business or holding assets?
Offshore entities can work well when you don’t need UAE local trading.
Do you want liability protection for shareholders?
An LLC is commonly chosen when reducing personal risk is a key concern.
Quick checklist before you pick a structure
- ✓
Market access: Will you trade inside the UAE mainland, or mainly export/re-export?
- ✓
Ownership preference: Do you want full foreign ownership from day one?
- ✓
Liability: Do you need shareholder liability capped to invested capital?
- ✓
Office needs: Do you need a physical office/warehouse, or a lighter setup?
- ✓
Growth plan: Branches, contracts, visas, and expansion goals should match the structure.
If you’re stuck between two options, a short consult can save time and rework.
Quick quiz: Which structure sounds closest to your plan?
Explore Mainland Companies
Mainland companies allow you to operate throughout the UAE without the geographic limitations often associated with free zones. These entities are established under the jurisdiction of the UAE government and must meet certain regulatory requirements set by the Department of Economic Development (DED) in the relevant emirate. For many entrepreneurs, a mainland company offers broad flexibility, letting you engage in both local and international business activities.
Mainland company snapshot
| Best for | Key advantage | Main limitation | What to watch |
|---|---|---|---|
| Businesses needing UAE-wide market access | Operate across the UAE and pursue broader activities | More direct compliance requirements vs many zones | Activity rules, approvals, and renewals by emirate/DED |
| Firms targeting government and public sector work | Better alignment for contracts and local operations | Documentation and compliance can be stricter | License classification and any capital/sponsor requirements |
Mainland Pros And Cons
- Pros
- Operate across the entire UAE market with no trade limitations.
- Access lucrative government contracts and public sector projects.
- Option to open multiple branches within the UAE and beyond.
- Cons
- Subject to local regulations and compliance requirements that can be stricter than free zones.
- You may need to meet specific capital or sponsor requirements, depending on your license and activity.
Steps To Form A Mainland Company
- Choose Your Business Activity: Determine your main offering, whether it’s retail, consulting, or manufacturing. Each activity dictates the specific license you’ll need.
- Obtain Initial Approval: Apply for preliminary clearance from the DED, confirming that your chosen activity and business name are permitted.
- Draft Legal Documents: Prepare a Memorandum of Association and any relevant legal agreements to define ownership percentages and management roles.
- Secure a Business License: Once your documents are in order, finalize the required fees and obtain a DED license.
- Complete Visa Processes: If you or your team need UAE residence permits, submit the relevant applications after you receive the license.
Mainland setup steps (quick expand)
Choose your business activity
Initial approval and name check
Legal documents (MOA and agreements)
License issuance + visas
After your mainland company is established, staying current on industry regulations and renewing your license annually is crucial. This is where compliance services and pro services can play a vital role. These specialized services help you keep pace with legal updates and manage any administrative requirements, such as trade license renewals or sponsor agreements.
Enroll In Free Zone Companies
Free zones are often considered a streamlined path for foreign investors seeking 100 percent business ownership without requiring a local sponsor. Each free zone has its own regulatory framework, but all offer a unique blend of tax benefits, streamlined customs processes, and tailored infrastructure. Ideal for those focusing on export or re-export activities, free zones can shield you from complexities like dealing directly with various local government entities.
Free Zone Pros And Cons
- Pros
- Full foreign ownership, letting you maintain complete control of your business.
- Tax advantages, including zero corporate tax in many free zones.
- Modern infrastructure and efficient administrative processes tailored to your industry.
- Cons
- Restrictions on doing business in the UAE mainland, so additional licensing might be needed if you plan to serve local customers.
- Each free zone has its own rules, which can differ significantly from one to another.
Free zone company snapshot
| Best for | Key advantage | Main limitation | What to watch |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foreign founders prioritizing full ownership | 100% foreign ownership + streamlined admin | Mainland trading restrictions may apply | Zone rules by industry, office requirements, visa quotas |
| Export/re-export and niche industry setups | Infrastructure tailored to sectors (IT, media, trade) | Rules can vary widely by free zone | Scope of permitted activities and renewal costs |
Key Steps For Free Zone Setup
- Select the Right Free Zone: Research various free zones to find the one that aligns with your industry, such as IT, media, or trade.
- Prepare Documents: Typically, you’ll need a copy of your passport, business plan, and proof of address, although the exact requirements vary.
- Obtain the License and Visa: Submit your application to the free zone authority along with the prescribed fees. If approved, you’ll receive your license and any associated visas.
- Lease or Purchase Space: Many free zones require you to have an office or warehouse facility as part of the registration.
- Open a Corporate Bank Account: After your license is issued, you can set up a dedicated corporate banking account to handle business transactions.
Free zone setup checklist (fast prep)
Documents: passport copy, proof of address, and any required business plan.
Activity match: confirm the zone supports your exact activity category.
Facility: check whether office/warehouse leasing is mandatory.
Visas: confirm how many visas you can get under your package.
Banking: plan for corporate account requirements and timelines.
If you plan to expand into the mainland market, you may need additional approvals. Comparing mainland vs free zone regulations can help you figure out which framework suits you best as your business grows.
Consider Offshore Companies
If your primary goal is to conduct international business or hold assets outside the UAE, an offshore company may be the right fit. Offshore entities are registered within the UAE but operate outside its borders. These companies typically don’t require a physical office space in the UAE and are exempt from many local regulations that affect mainland or free zone businesses.
Offshore Pros And Cons
- Pros
- You can enjoy confidentiality and asset protection benefits, valuable for international trade or company holding structures.
- No requirement to rent local office space, which can significantly reduce overhead.
- Potential tax advantages in terms of corporate or income taxes, depending on your specific home country regulations.
- Cons
- Offshore companies often cannot do business within the UAE market.
- You may need professional guidance to understand how different tax treaties and compliance rules affect your international operations.
Getting Started With An Offshore Company
- Choose an Offshore Jurisdiction: Popular jurisdictions include Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA Offshore) or Ras Al Khaimah International Corporate Centre (RAK ICC).
- Submit Necessary Documents: This can include your passport, proof of address, and bank references, depending on the offshore authority’s rules.
- Draft Memorandum And Articles of Association: Outline the purpose and structure of your offshore business.
- Open an Offshore Bank Account: While not mandatory in all cases, a dedicated business account simplifies your international transactions.
- Maintain Regular Compliance: Even though offshore entities have fewer obligations, you still need to file annual reports or updates to stay valid.
Offshore companies: quick clarity
What offshore is usually used for
What offshore usually cannot do
What you’ll typically prepare
For procedures like official translations, notarizations, or attestation, pro services can guide you through legal complexities. You’ll also want to consult tax consultancy professionals if you plan to manage cross-border tax issues and ensure you’re in compliance with global regulations.
Form Limited Liability Companies
When you set out to form a Limited Liability Company (LLC) in the UAE, you’ll find it shares some characteristics with mainland registration, particularly if you opt for an onshore LLC in an emirate’s jurisdiction. However, the LLC structure also applies within certain free zones, simply referred to as a Free Zone LLC. In general, LLCs limit shareholder liability to their stakes in the company, reducing personal risk.
LLC Pros And Cons
- Pros
- The liability of each shareholder is capped to their respective capital contribution.
- If you choose a free zone LLC, you can enjoy 100 percent foreign ownership in that zone.
- Flexibility in management, as all shareholders can be actively engaged in running the company.
- Cons
- Setting up a mainland LLC previously required a local sponsor, although recent reforms introduced 100% business ownership for certain activities.
- You’ll need to follow ongoing company compliance procedures, which may include annual audits and regulatory renewals.
LLC snapshot
| Best for | Key advantage | Main limitation | What to watch |
|---|---|---|---|
| Founders wanting capped personal risk | Liability limited to capital contribution | Ongoing compliance and renewals | Activity eligibility, audits (where applicable), and renewals |
| Scaling into regulated or growth industries | Flexible management and expansion options | Setup route differs by mainland vs free zone LLC | Choose the jurisdiction that matches market access needs |
Steps To Form An LLC
- Determine LLC Type: Decide whether you want an LLC on the mainland or in a free zone. Evaluating cost to form an llc can help you budget effectively.
- Select Your Business Activity: Similar to other structures, the type of activity informs your license classification (commercial, professional, or industrial).
- Submit Registration Documents: Provide personal identification, a NOC (if required), and your LLC’s Memorandum of Association.
- Pay the License and Registration Fees: Fees vary depending on the emirate and whether you choose a free zone or mainland option.
- Collect Your Trade License: Once approved, you can begin operating officially, whether you plan to target local customers or international markets.
If you dream of scaling quickly or aiming for specialized industries like e-commerce or crypto trading, an LLC gives you the adaptability to expand in line with evolving regulations. You can also explore crypto trading business license in the uae for more information on entering that emerging market.
Establish Branch And Representative Offices
Branch and representative offices let you extend an existing foreign company’s presence into the UAE without creating a separate legal entity. While these structures serve different functions, both can help you tap into the UAE market and showcase your brand to local customers.
• A branch office can perform business activities similar to its parent company, generate revenue, and sign contracts.
• A representative office focuses on marketing or research for the parent company, but it cannot conduct profit-making activities in the UAE.
Branch vs representative office (simple comparison)
| Type | What it can do | Revenue in UAE | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Branch office | Operate like the parent company and sign contracts | Yes (within licensed scope) | Testing UAE market while keeping parent-company identity |
| Representative office | Marketing, promotion, and research for the parent company | No (non-profit-making) | Brand presence and lead generation without trading |
Branch And Rep Office Benefits And Challenges
- Benefits
- Quick market entry to test local demand before committing to a separate entity.
- Utilize the parent company’s reputation and resources for branding and operational efficiency.
- Opportunity to build strategic partnerships in the UAE without a fully fledged subsidiary.
- Challenges
- No separate legal identity, so the parent company remains liable for branch or representative office debts.
- Regulatory approvals and licenses depend heavily on the scope of activities you plan to run locally.
Setting Up A Branch Or Rep Office
- Secure Initial Approval: Approach the relevant UAE authority with details about your parent company’s background and proposed activities.
- Sign A Local Service Agent Agreement (If Needed): In some cases, you must appoint a local service agent to assist with administrative tasks.
- Obtain Your License: A commercial license for a branch office or a professional license for a representative office, subject to the activity type.
- Collect Visas For Staff: If your team members need to work in the UAE, sponsor their residency or business visas.
- Maintain Your Office Space: Although branch offices can sometimes rent smaller spaces, you still need a physical address in the emirate.
Branch / rep office setup steps (quick expand)
Initial approval
Local service agent (if needed)
License + visas + office
Because branch and representative offices represent an extension of the parent company, you’ll need to track any changes in your home country’s policies or corporate structure. Compliance can become more sizable, so you may benefit from specialized concierge services or accounting and bookkeeping solutions.
Conclusions And Next Steps
Selecting the right business structure in the UAE can accelerate your path to growth and profitability. Whether you prefer the versatility of a mainland company, the benefits of a free zone entity, the global reach of an offshore firm, the liability protection of an LLC, or the streamlined presence of a branch or representative office, you’ll find an option to suit your goals. By understanding the requirements, advantages, and potential challenges of each structure, you’ll be better prepared to make an informed decision.
Final recap: pick the structure that fits your plan
- ✓
Mainland: best when UAE-wide local market access is the priority.
- ✓
Free zone: strong for full foreign ownership and zone-based industry support.
- ✓
Offshore: useful for international structures and holding assets (not local trading).
- ✓
LLC: common choice when you want capped liability and flexibility.
- ✓
Branch/Rep: for extending an existing foreign company presence into the UAE.
If you’re not entirely sure which direction to take, consider consulting local experts who understand the administrative nuances in each emirate. They can guide you through how to setup a business in the uae, from license applications to annual renewals. You can also explore cost-efficient tips for specific situations, such as how to start a business with no money or ways to handle expansions beyond the UAE market.
Ultimately, your choice depends on where you see your venture headed in the coming years. Whether you plan on scaling rapidly, staying lean, or focusing on niche markets, the UAE’s welcoming environment offers ample freedom to tailor your business for success. By leveraging the right structure, you’ll be in a prime position to attain a strong market presence, forge strategic partnerships, and secure long-term profitability in one of the world’s most dynamic business hubs.
Need help choosing the right UAE business structure?
Tell us your activity and goals, and we’ll guide you to the setup that fits your ownership, licensing, and growth plan.